A Century of Insurance Journal
See the past 100 years in Insurance History.
100 Years in Insurance and the Moments We've Seen …
As 2023 — Insurance Journal's 100th anniversary year — comes to a close, we looked back at the past 100 years in insurance history.
The following pages reflect 100 moments in history that changed the insurance industry including the first state to require auto insurance, the passage of the McCarran-Ferguson Act in 1945, and the unimaginable tragedy on 9/11.
We invite you to join us in a look at 100 key moments in time that shaped today's insurance world. As part of this report, we asked a few thought leaders to share their views on the past 100 years in insurance as well. We hope you enjoy this look back in time.
Everyone at Insurance Journal wishes you a happy holiday season and a prosperous new year.

In thinking about the insurance industry and what's occurred over the past 100 years, the biggest change in my opinion has been in the attitude shift towards the intermediary. In the 1980s and 1990s, conventional wisdom was that the insurance agent and broker was going to be a disintermediated, that with technology innovation, carriers were going to go direct to insureds bypassing the agent and broker. There was a lack of investment in insurance brokerages during this time. All of this flipped with the .com bust in 2000. Technology was not the answer, but the value add that an agent and broker brings to a client with their advice and advocacy was really important. With this shift and realization, the advent of the global broker came to be. In the 1980s and 1990s, there were really only two large brokers and no real global broker. Since 2000, there are now numerous global brokers, and investment money is flowing into this sector. This attitude shift is what I believe has been the major change in the industry over the past 100 years. In my opinion, the US agent and broker is the most valuable asset in the insurance industry.

The Year of the Retail Breach, in 2014, propelled cyberattacks onto the list of most-dreaded risks for businesses. The Target credit card breach in December of 2013 sent ripples of disruption into 2014, then Home Depot was hit in summer of 2014. Hackers behind both of these cyber breaches, within months of each other, exploited a similar vulnerability and put corporate America on notice that the responsibility for cyber resilience does not rest solely with IT. The extent of the impact – Target paid $18.5 million in multistate legal settlements alone — shocked and awed Americans into paying attention and, in the case of businesses, taking action. The number of companies purchasing standalone cyber policies leapt 32% in the first half of 2015, according to a Marsh report, and prices for coverage climbed, especially for industries that had been victims of an attack.

While many people point to the McCarran-Ferguson Act of 1945 as the most significant piece of federal legislation impacting the insurance industry over the past century, the reality is that McCarran-Ferguson would never have come into existence were it not for the shocking decision against the industry by the U.S. Supreme Court in the case of the United States vs. South-Eastern Underwriters Association just one year earlier (1944). In that case, the court found that the industry was in violation of federal antitrust law. The decision seemed to reverse precedent established 75 years earlier with the Supreme Court's 1869 decision in Paul v. Virginia Supreme Court 1869, in which the Court had determined that insurance is not interstate commerce and thus is subject to regulation by states as they see fit. The McCarran-Ferguson Act was passed one year later in 1945 to address the apparent contradiction related to the primacy of state versus federal regulation.
Another critical event, according to Hartwig, was the inception of the NFIP.
The National Flood Insurance Act of 1968 launches the NFIP with two primary goals: reducing future flood damage and protecting property owners. The latter goal was necessitated by virtue of the fact that private insurers did not and would not include flood damage in their standard homeowners insurance policies. The NFIP's track record has been very mixed. While millions of homeowners have benefitted from the ability to purchase NFIP coverage, policies were routinely underpriced resulting in tens of billions of dollars in losses in excess of premiums — losses which are ultimately born by taxpayers. More than a half-century of underpricing has also encouraged rampant development in flood-prone areas throughout the country.

The COVID pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work and digital technologies across the insurance industry. Companies had to quickly adapt to remote work environments to ensure business continuity. Digital tools and platforms became a necessity, leading to increased investment in technology and digital transformation. Overall, the pandemic prompted a reevaluation of business processes and emphasized the importance of workforce adaptability and resilience. Signs indicate the effects of the pandemic will be long-lasting:
- Flexible work hours and location have become essential to attract and retain talent. This shift has forced companies to rethink company culture and the mentoring of new hires.
- Insurers continue to invest in technology to improve operational efficiency, enhance the customer experience, and support a dispersed workforce.
- Continuity planning is now front and center at insurance companies. Insurers are now applying their risk mitigation expertise to their own businesses to prepare for potential threats.

Hurricane Andrew was the single most significant event to impact the insurance industry during my career. For me personally, as someone who was born and raised in Miami, it was shocking to witness the absolute destruction brought by this storm. No one knew what a Category 5 storm could do, and in many ways, it changed the face of the city forever. Andrew brought attention to aggregate management, as many insurance companies were completely unaware of how much exposure they had in South Florida. Unfortunately, this led to numerous insurance bankruptcies. Not only did it reshape the entire insurance landscape, from reinsurance to regulations, Andrew also changed the housing industry and South Florida building codes, which became stronger and more stringent.

On, April 1, 1960, NASA launched the first functional meteorological satellite, TIROS-1, in the world. Given the increasing impact of weather on property losses, not to mention life safety, today, the ability to observe the previously unobservable has proven to be instrumental in loss prevention and reduction of weather-related risks.
Then in 1971, Insurance Services Office (ISO) was formed by combining dozens of state and regional rating, inspection, and actuarial bureaus into one organization. That was a remarkable accomplishment…I can't think of any industry that, to my knowledge, ever accomplished something like that. The value of ISO as an industry coverage standard setter cannot be understated. I tell people I'm older than ISO since in entered the industry, in fact, working for an ISO predecessor, the Tennessee Inspection Bureau.

For HUB, the last 25 years has seen unprecedented and increasing complex risks, from the AIG bailout and the financial crisis in 2008, which completely changed the insurance landscape, to the explosion of insurtech and the emergence of digital platforms in 2014, to the increase of catastrophic events, including Hurricanes Andrew, Katrina and Sandy, which changed building codes, deductible and policy structures. But, for me, nothing compares to 9/11. It stands out not only as the impetus for TRIA (Terrorism Risk Insurance Act), which continues to be a vital risk transfer mechanism for clients, especially those in densely populated urban areas like New York City, but also because of the human tragedy and loss of life. It was directly felt in the financial and insurance sectors with many colleagues lost that day and the shattering feeling of insulation in the U.S. from terrorism.
1920's

1923
Insurance Journal launches its first print publication to cover the California insurance market.

1925
Massachusetts becomes first state to require automobile insurance.

1926
Farm Bureau Mutual Automobile Insurance Co., now Nationwide, sells first policy.
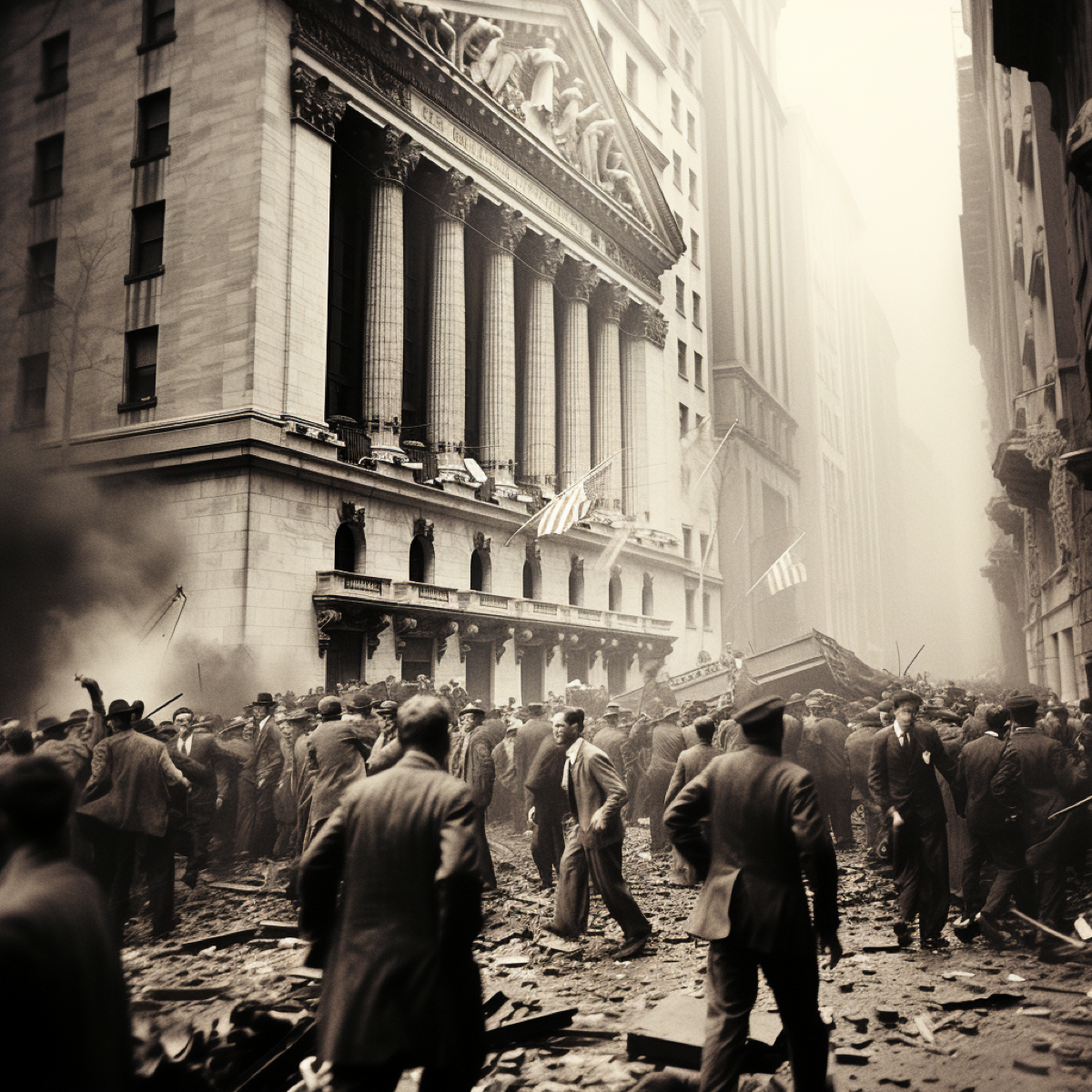

1929
Black Tuesday: Stock Market Crash occurs on Oct. 29, 1929, marking the start of the Great Depression.
1929
Chubb & Son begin underwriting aviation risks.
1930's

1931
Allstate Insurance Co. formed as a subsidiary of Sears & Roebuck Co.
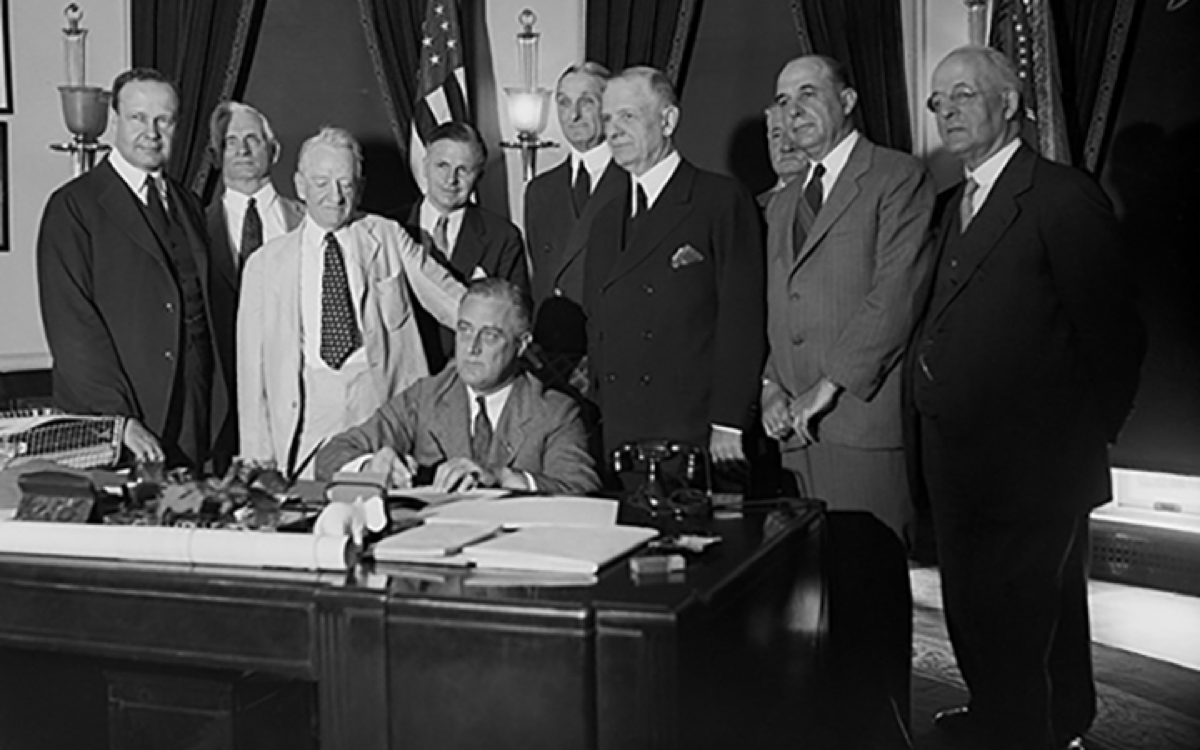

1933
The Banking Act of 1933 establishes the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp.

1933
Securities Act of 1933 and Securities and Exchange Act of 1934 increase regulations and liabilities of financial institutions, and lead to development of directors & officers insurance policies.

1936
The Government Employees Insurance Co. (GEICO) is established to provide auto insurance to federal employees and military personnel.
1937
Progressive Mutual Insurance Co. founded to provide auto insurance, open's first drive-in claims location.
1938
The Federal Crop Insurance Act enacted to help the agriculture industry.

1939
Allstate becomes first insurer to tailor auto rates by age, mileage and car usage.

1939
Great Depression ends.
1940's
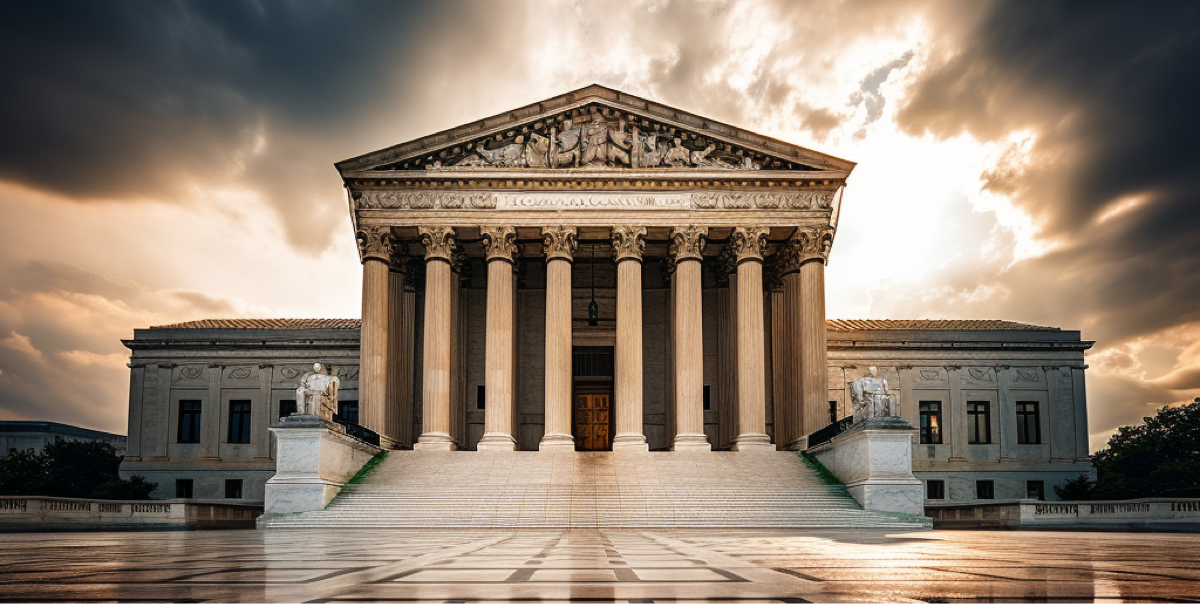

1944
U.S. Supreme Court determines insurance industry should be federally regulated in U.S. v. Southeastern Underwriters Association.
1945
McCarran Ferguson Act passed, returning insurance regulation to individual states.

1947
New York establishes Motor Vehicle Liability Security Fund to cover auto insurance company insolvencies.

1948
Mississippi becomes last state to enact a workers' compensation law.
1950's

1950
First homeowners insurance package policy introduced to incorporate multiple lines of coverage in one policy.

1951
Warren Buffet makes first purchase of GEICO stock.

1954
South Dakota begins issuing driver's licenses, the last state to do so.

1955
Farm Bureau Mutual Insurance Co. becomes Nationwide Insurance.
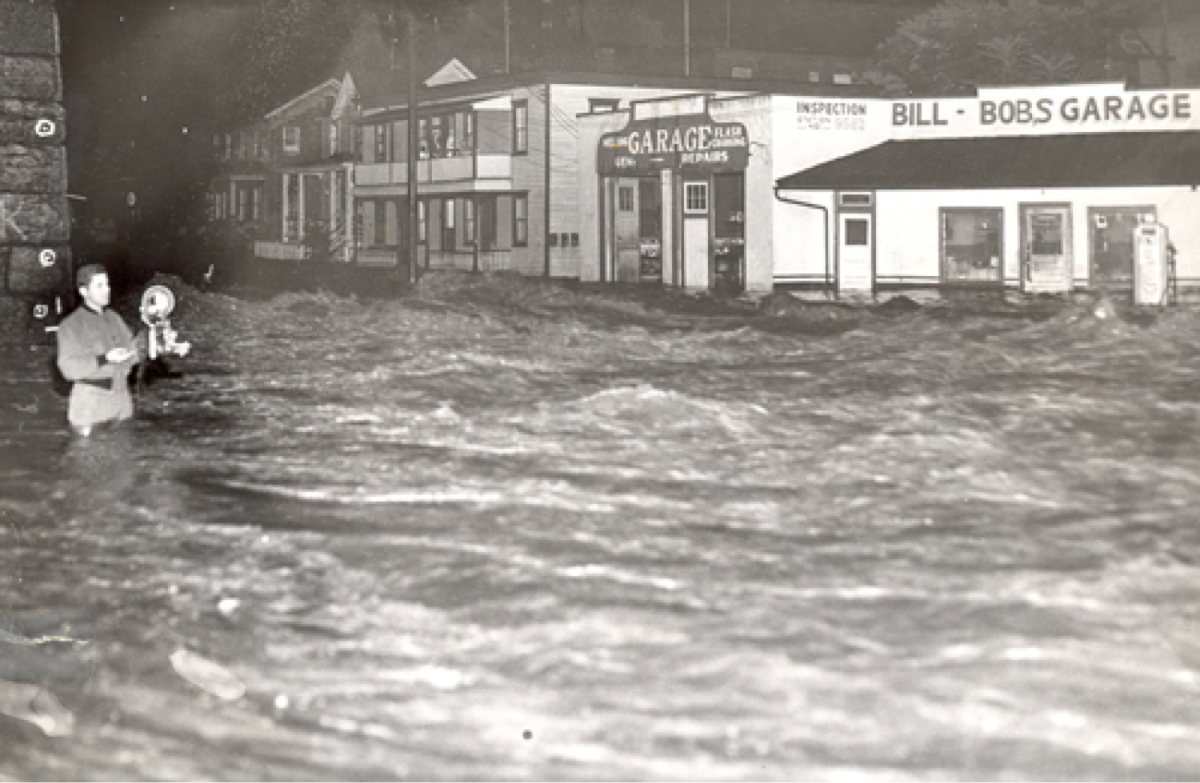

1955
Hurricane Diane hits the northeastern U.S., becoming costliest hurricane in history at the time.
1956
Progressive Casualty Insurance Co. forms as the first specialty underwriter of nonstandard insurance.

1956
Black insurance agent Theodore Martin Alexander arranges for Lloyd's to cover auto policies of black drivers' driving carpools during Montgomery, Ala., bus boycott.

1959
Auto insurance industry forms Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS).
1960's

1963
Nationwide begins offering medical benefit incentive to policyholders wearing seatbelts in an automobile accident.

1964
Civil Rights Act passed, prohibiting discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.

1965
Lloyd's of London syndicates provide first space satellite insurance.
1965
Hurricane Betsy becomes the first Atlantic storm to cause at least $1 billion in damages.

1967
Warren Buffet's Berkshire Hathaway makes the first insurance company acquisition, National Indemnity Co.

1967
American International Group, Inc. (AIG) incorporates in Delaware.

1968
The National Flood Insurance Act is passed, establishing the National Flood Insurance Program.
1970's

1970
The Fair Credit Reporting Act is enacted, requiring insurers to notify consumers if an adverse action is taken because of credit information.
1972
W.R. Berkley Corporation enters the insurance market through the acquisition of Houston General Insurance Co.

1976
Berkshire Hathaway purchases 1 million shares of GEICO stock.
1978
First environmental impairment liability insurance introduced to fill pollution coverage gaps.
1980's

1980
Comprehensive Environmental Response and Liability Act of 1980 imposes cleanup liability on polluters.
1981
The Product Liability Risk Retention Act is enacted to allow the formation of self-insurance risk retention groups (RRGs).

1982
First pet policy issued in the U.S. by Veterinary Pet Insurance.
1983
U.S. Supreme Court rules in favor of automobile insurance industry in lawsuit against the federal government for rescinding the requirement that new cars be equipped with airbags or automatic seat belts.
1985
Liability insurance crisis begins and lasts around 3 years.
1985
American Casualty Excess Insurance Co. and ACE Limited form.
1986
Insurers tighten general liability policy wording to exclude nearly all pollution losses.
1986
Liability Risk Retention Act (LRRA) amends and expands the Product Liability Risk Retention Act of 1981 to increase the availability of commercial liability insurance.
1986
AIG introduces the first contractors pollution liability policy.
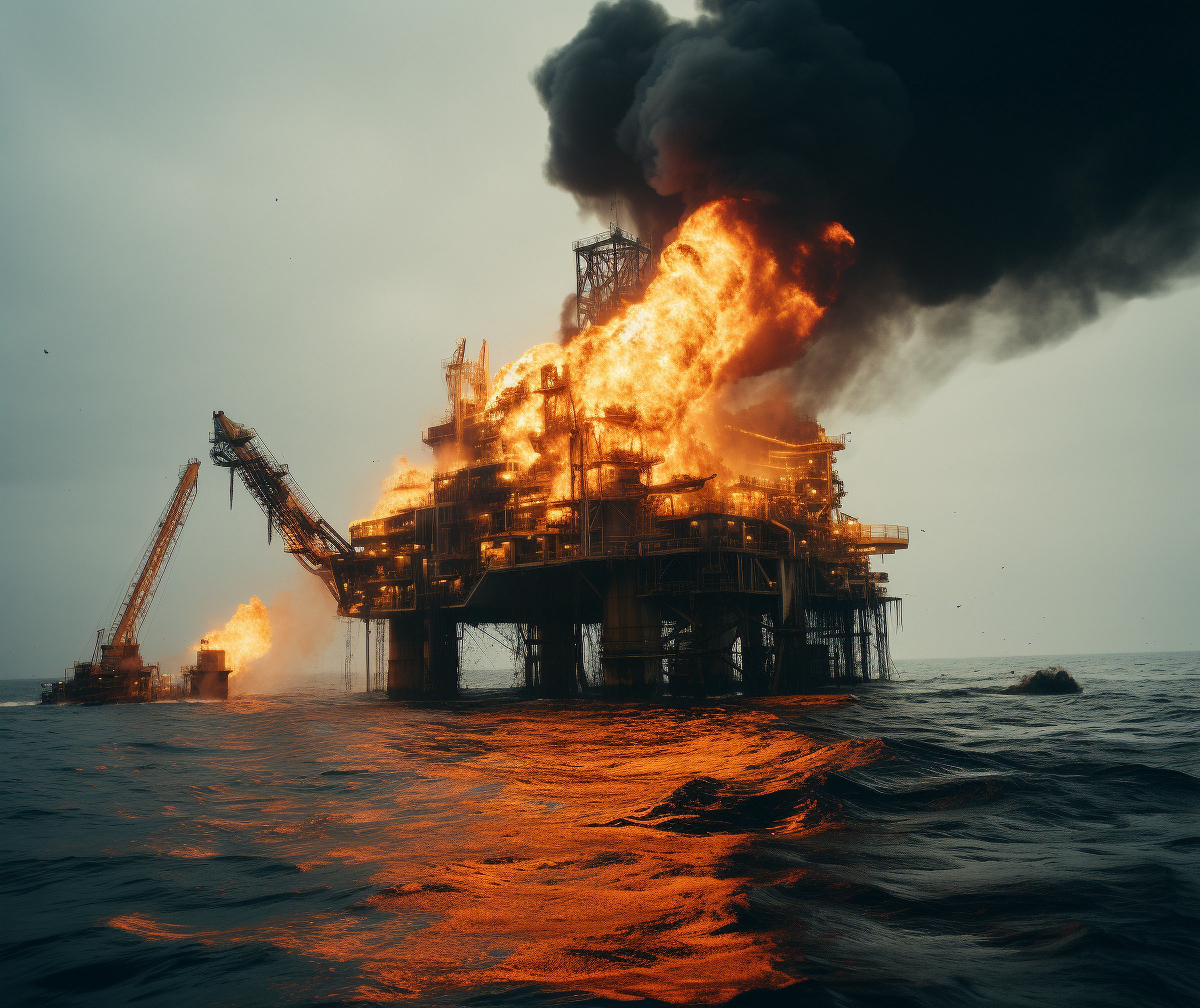

1987
Piper Alpha offshore oil disaster in North Sea becomes industry's costliest man-made catastrophe at the time.
1987
Karen Clark creates first catastrophe model and founds first catastrophe modeling company
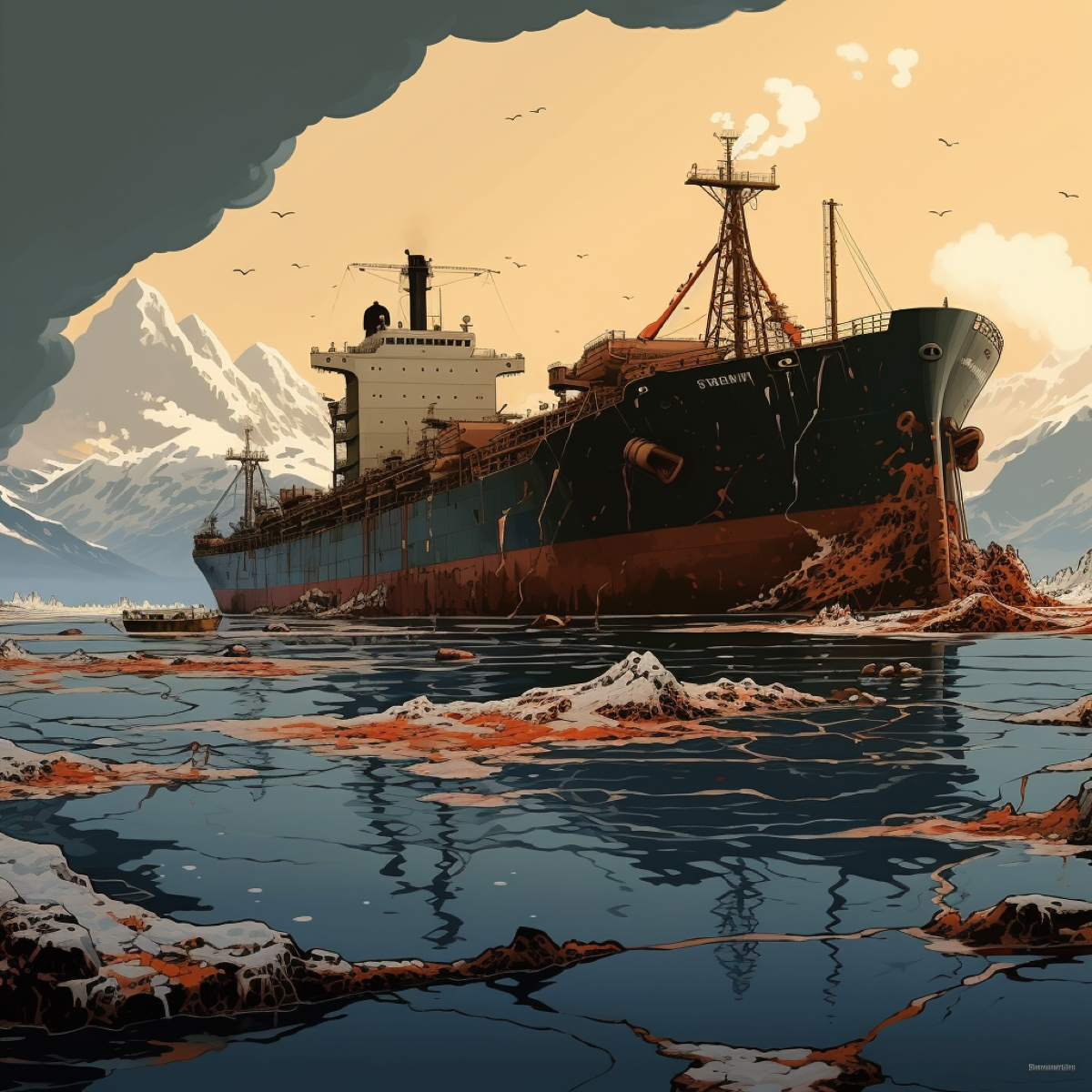

1989
Exxon Valdez oil tanker spills 11 million gallons of oil off Gulf of Alaska, becoming one of the largest environmental disasters in U.S. history.
1989
6.9 magnitude Loma Prieta earthquake causes $10 billion in damage in Northern California.
1990's
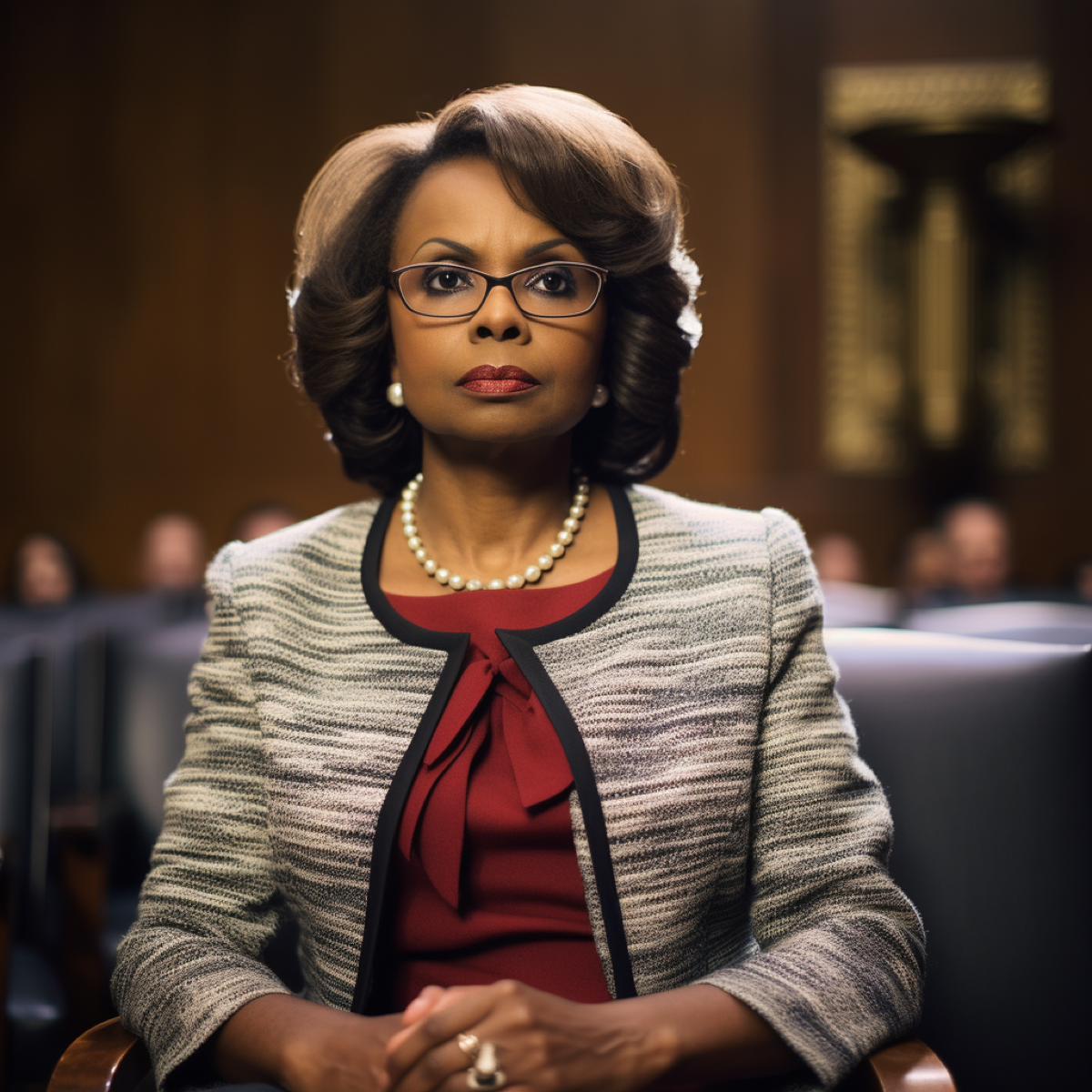

1991
Anita Hill testimony at Supreme Court Justice Nomination hearing for Clarence Thomas sparks action over sexual harassment in the workplace and passage of Americans with Disabilities Act and Civil Rights Act of 1991 leading to the evolution of employment practices liability insurance (EPLI).
1992
Hurricane Andrew slams into South Florida as the costliest hurricane to ever hit the U.S. (at the time).

1993
Allstate becomes a publicly traded company with the largest IPO in U.S. history.
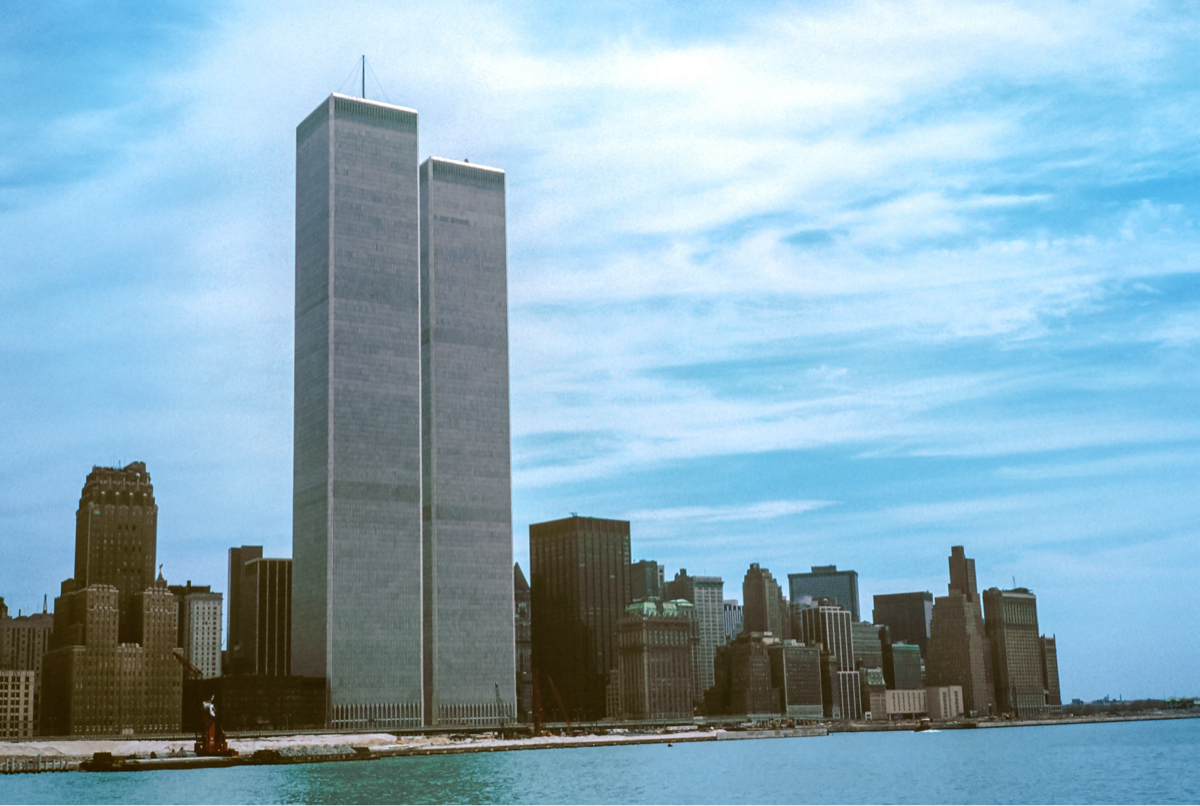

1993
World Trade Center bombing marks the first major act of international terrorism on U.S. soil.
1994
6.7 magnitude Northridge Earthquake hits Southern California.
1995
Progressive launches the first auto insurance group website, auto-insurance.com.
1996
GEICO becomes a subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway.
1997
Insurers begin utilizing telematics in auto insurance underwriting.
1997
Progressive becomes the first insurer to enable policyholders to quote and buy auto insurance online.

1997
The first cyber insurance policy is introduced for information technology companies.

1998
Google Inc. founded in Mountain View, Calif.
1999
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) enacted, requiring insurers to explain information-sharing practices with consumers and safeguard sensitive data, and for states to establish uniform requirements for the insurance producer-licensing process.
2000's

2000
The GEICO Gecko is introduced in television advertising.
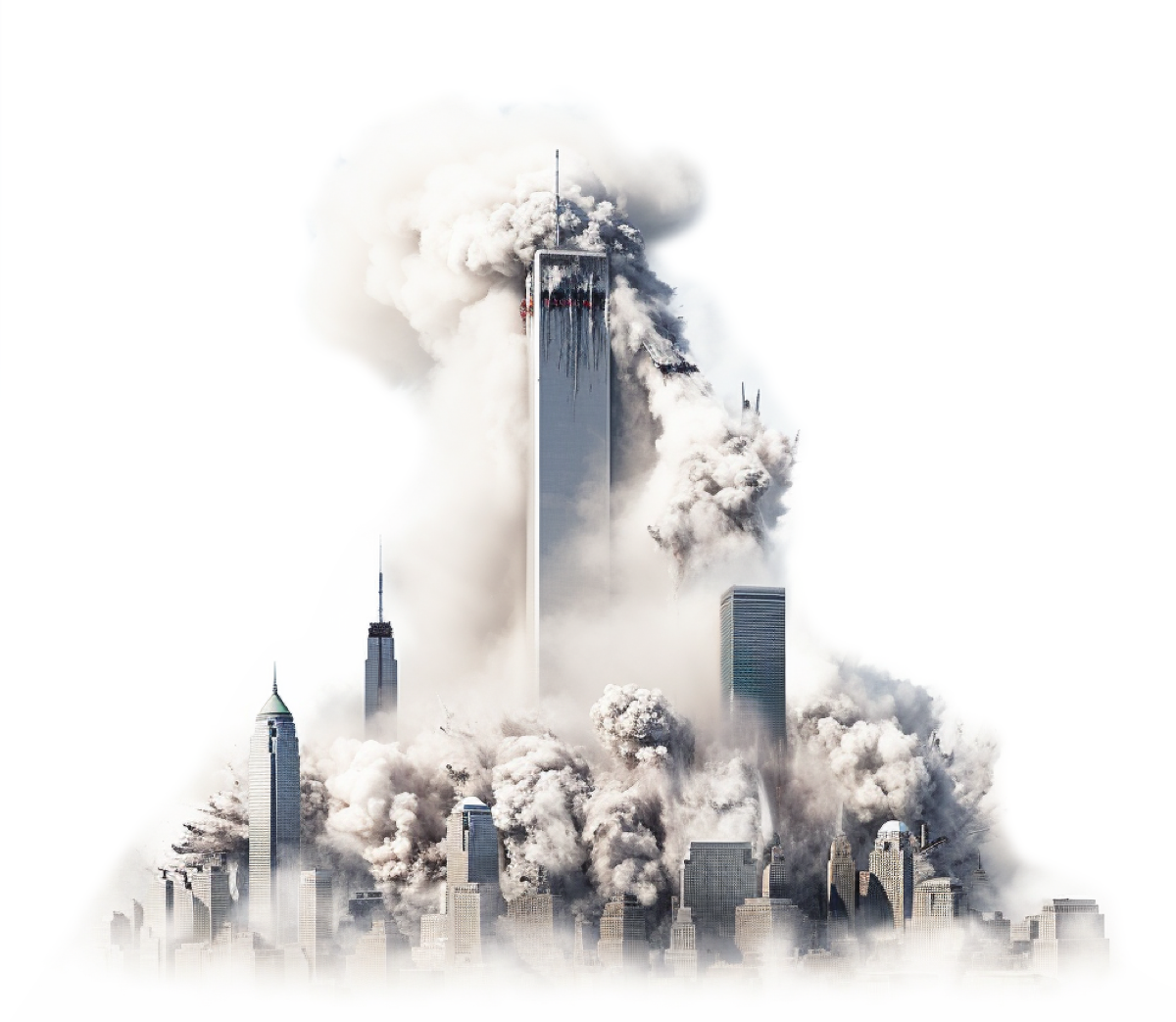

2001
Sept. 11 terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center in New York City and the Pentagon in Washington, D.C.
2002
The Terrorism Risk Insurance Act is enacted.
2004
Four Hurricanes – Charley, Frances, Ivan, and Jeanne – hit Florida in a six-week period.
2004
Progressive pilots usage-based auto insurance program in Minnesota.
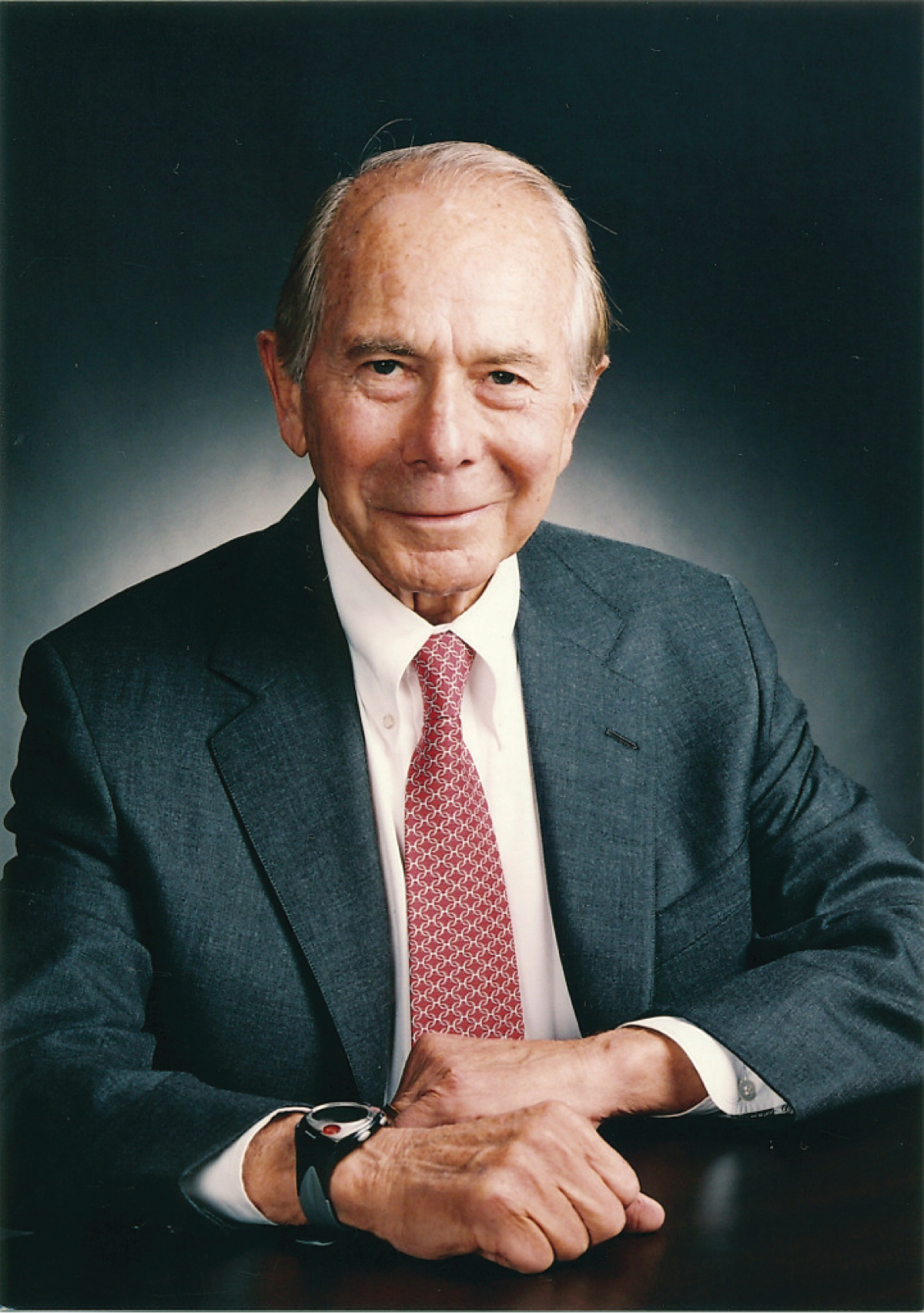

2005
Maurice “Hank” Greenberg leaves AIG after a 40-year relationship with the company.
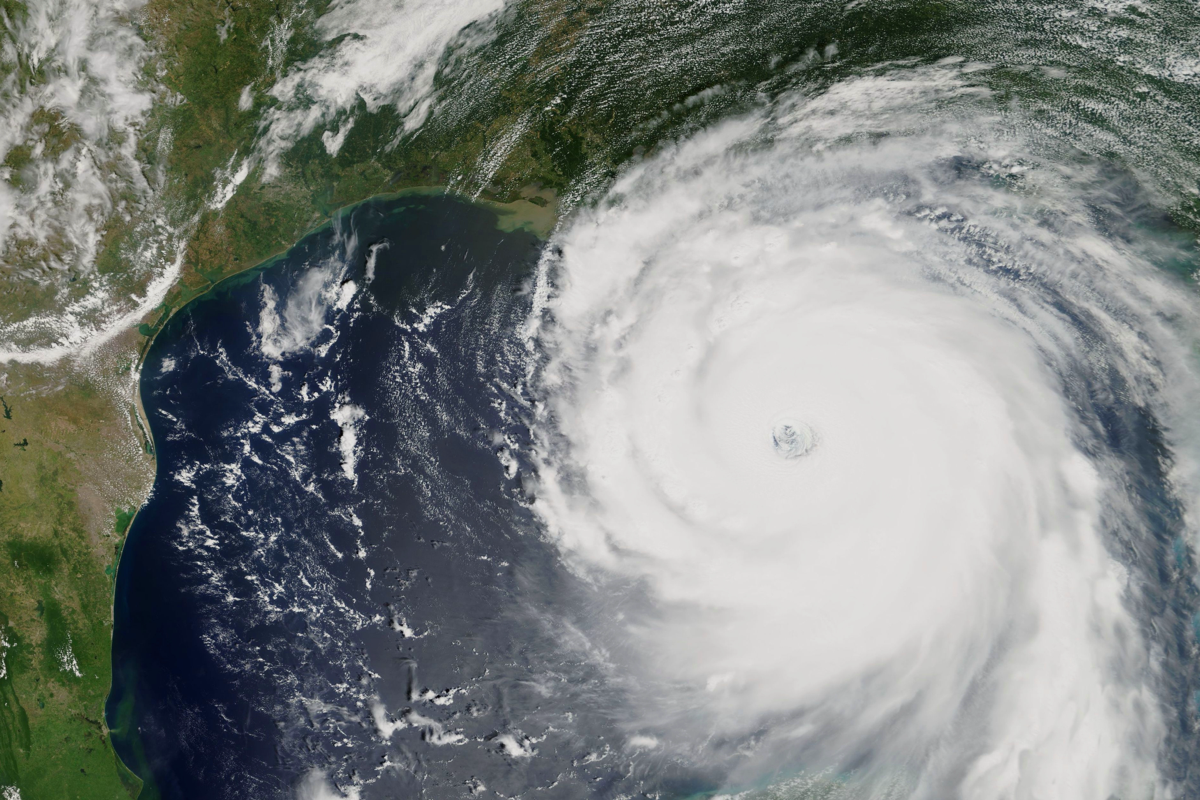

2005
Hurricane Katrina strikes Gulf Coast.

2006
Florida's Citizens Property Insurance Corp., the state-run insurer of last resort, becomes the state's largest property insurer after a mass exodus of private companies.

2008
Great Recession financial crisis leads to the U.S. Government's $85 billion bailout of insurance giant AIG.
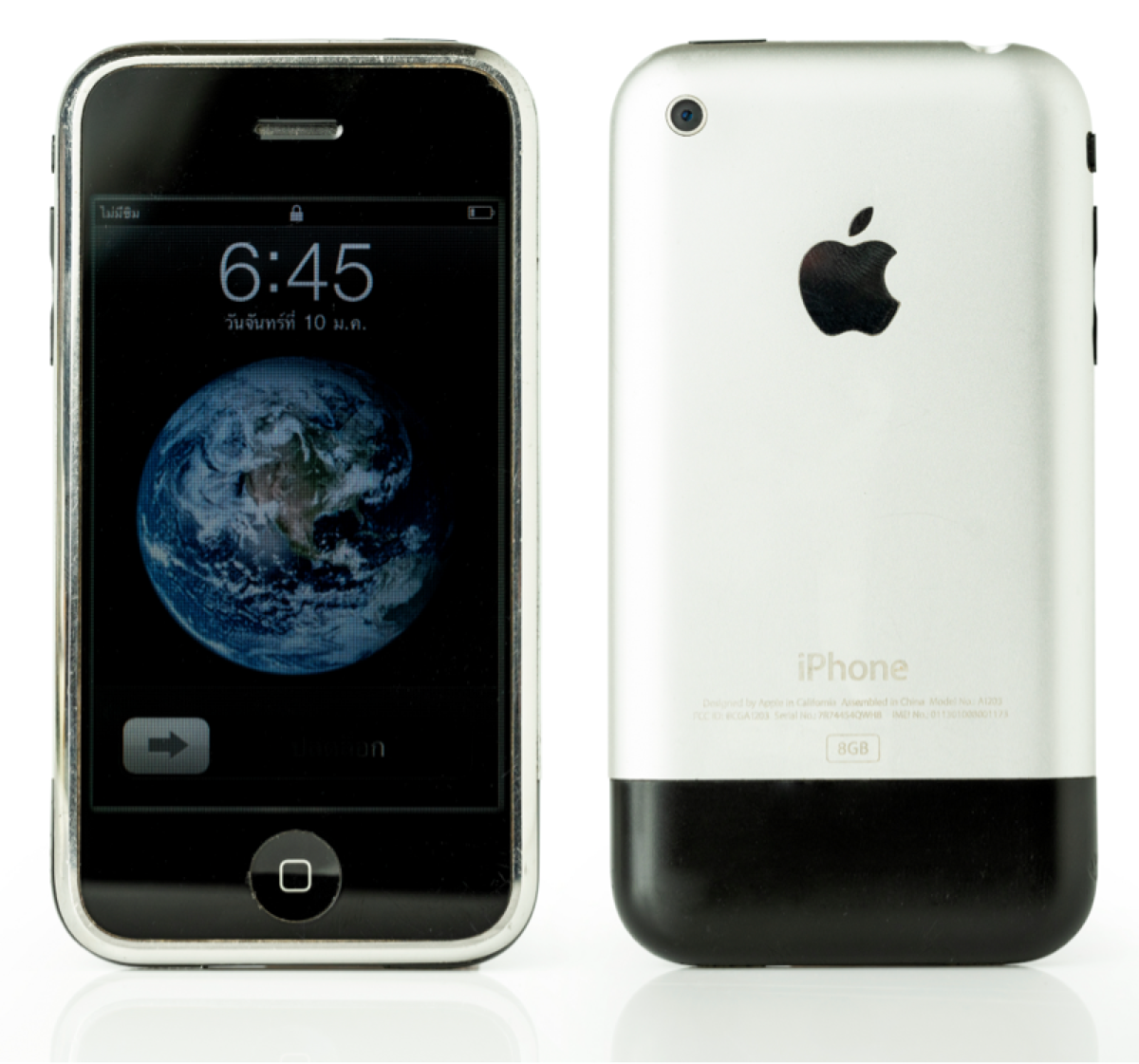

2009
Nationwide launches iPhone app for customers to process claims, find agents, and receive quotes.
2010's
2010
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act completely overhauls regulation of the financial services industry and establishes the Federal Insurance Office.
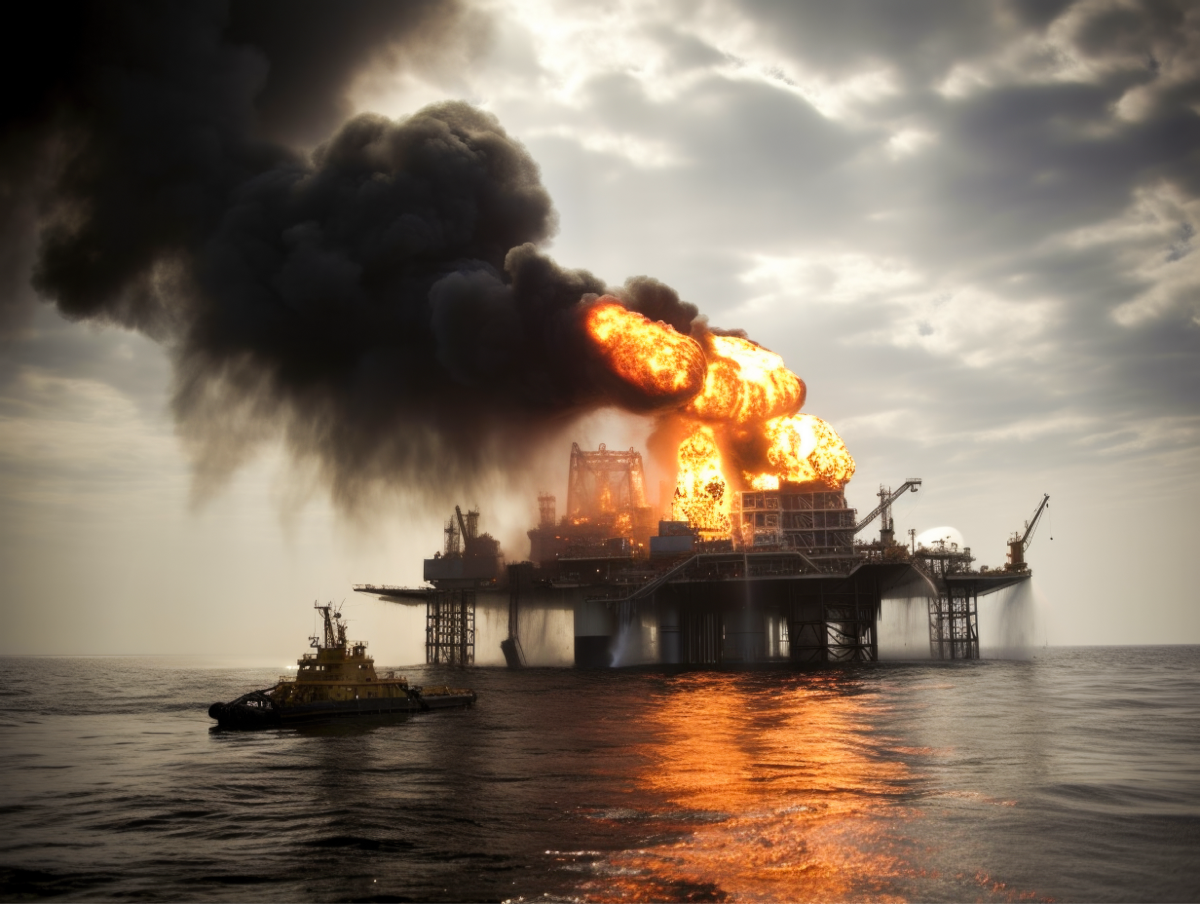

2010
Deepwater Horizon oil drilling rig explodes and sinks off Gulf Coast, becoming the largest oil spill in history.
2010
GEICO is the first insurer to enable quoting and buying coverage from smartphones.
2010
Insurance technology phenomenon now known as insurtech begins to advance across the industry.
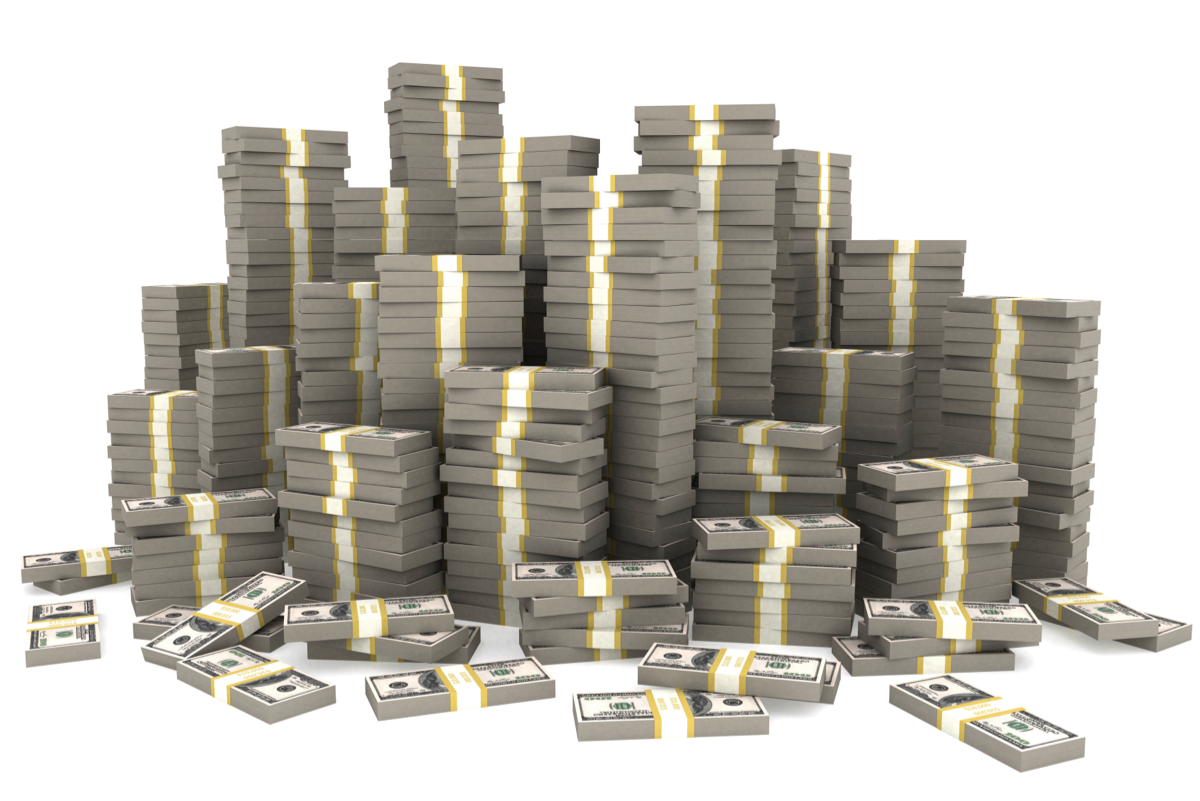

2012
AIG repays U.S. Government a total of $205 billion for support provided during the 2008 financial crisis.
2012
Hurricane Sandy causes $86 billion in damages across 24 states.

2013
Cyberattack on major retailer Target exposes personal and financial information of 110 million people, costing the company $202 million, including an $18.5 million settlement paid to individual states.
2014
10,000 gallons of chemicals used to process coal spill from a storage tank into Elk River used for drinking water in West Virginia.

2014
Inga Beale becomes the first female CEO in Lloyd's 300+ year history.
2014
Allstate introduces the first mobile telematics app.
2016
Lloyd's launches the first electronic placing platform to exchange information and transact business.

2016
ACE Limited acquires Chubb International for $28.3 billion, adopting the Chubb name.
2016
Hurricane Hermine breaks Florida's record 11-year hurricane drought.
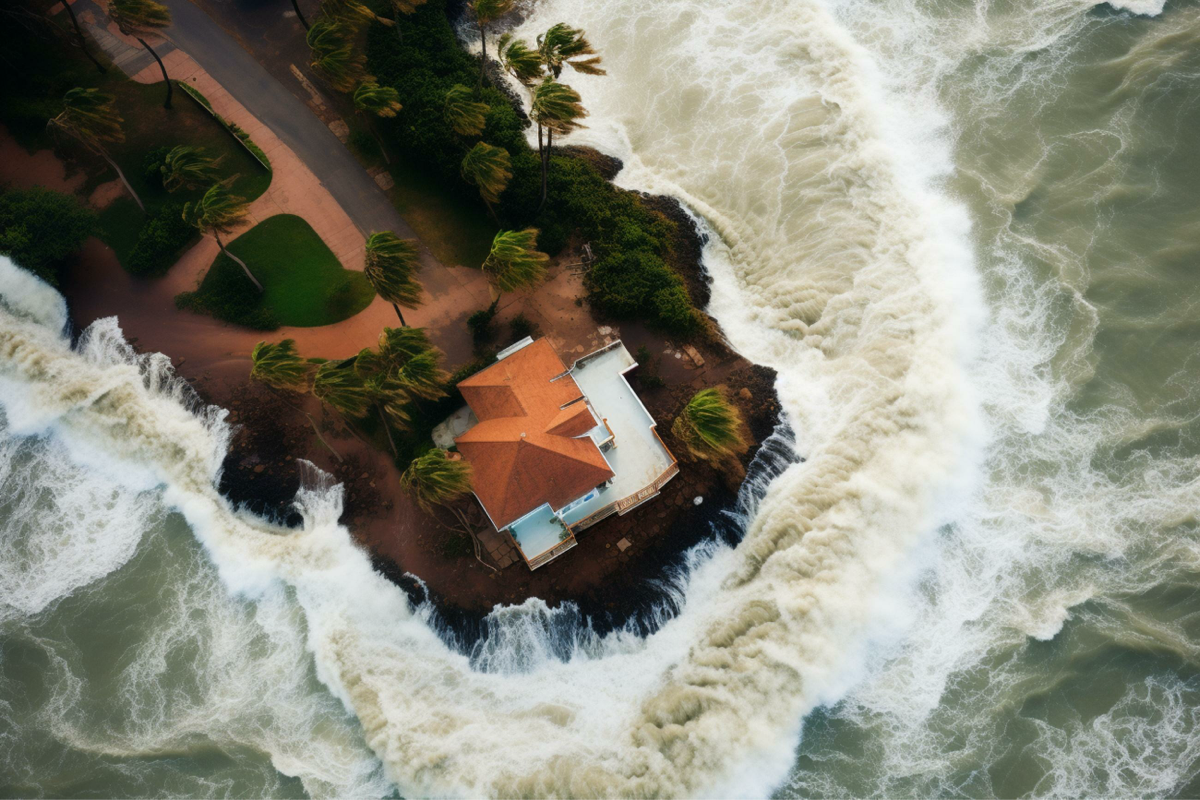

2016
Hurricane Matthew causes deadly flooding across the Carolinas.
2017
One of the most active Atlantic hurricane seasons on record, with 17 named storms, 10 hurricanes and 6 major hurricanes.
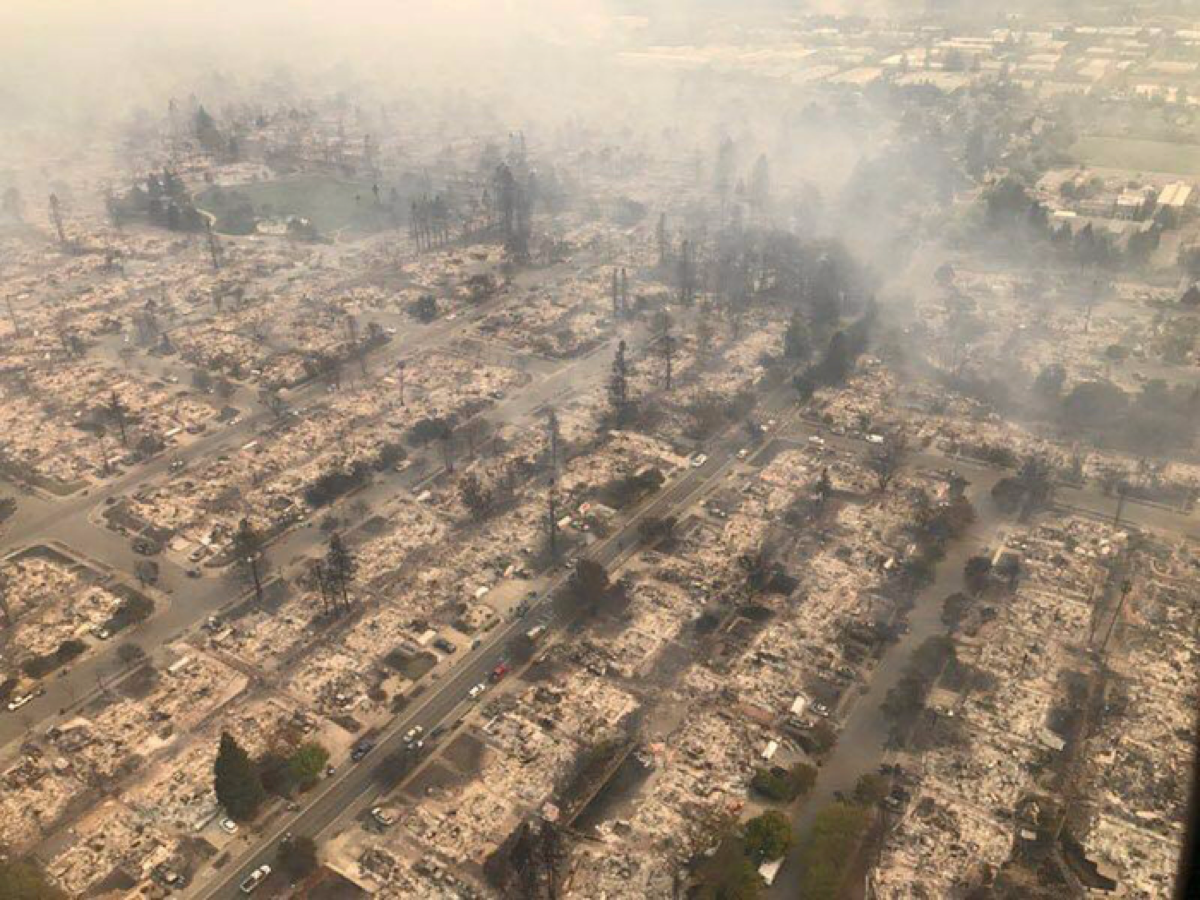

2017
California Tubbs Fire destroys more than 5,600 structures in Sonoma and Napa Counties.

2017
Sexual harassment and sexual assault allegations against film producer Harvey Weinstein ignites #MeToo movement and wave of EPLI lawsuits against executives.
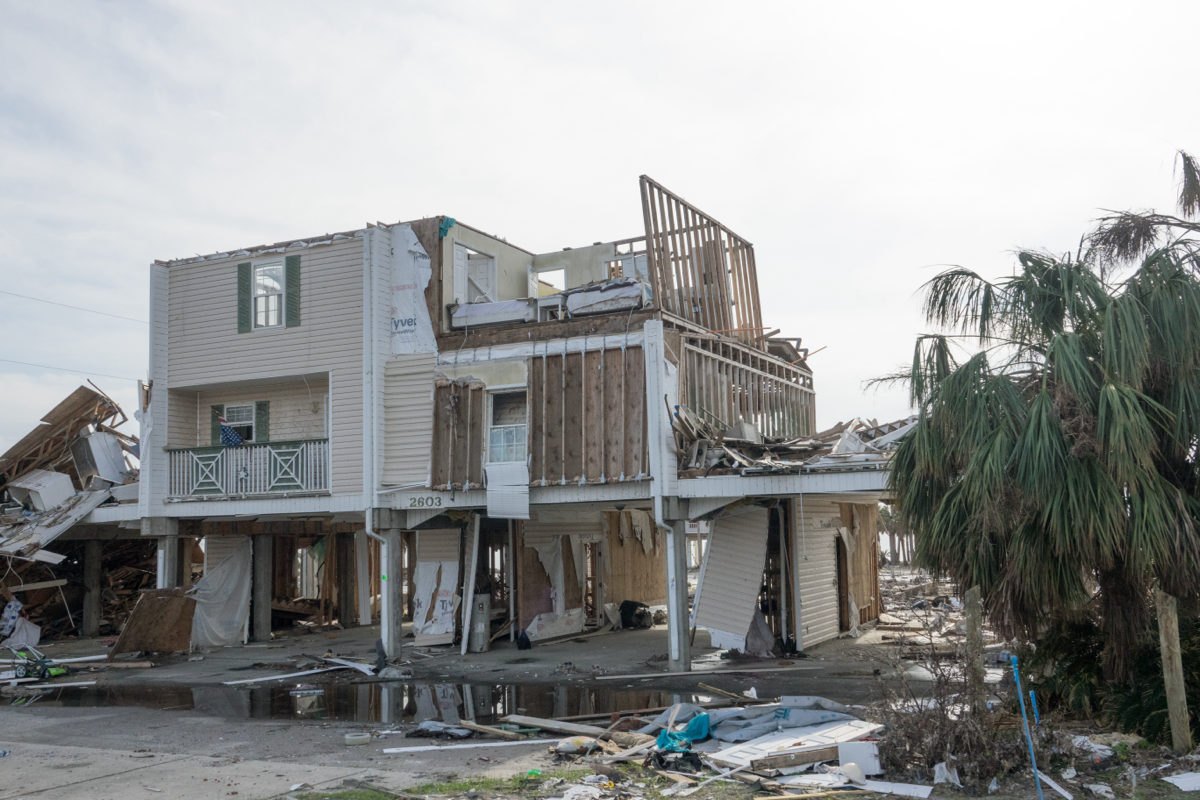

2018
Category 5 Hurricane Michael becomes the largest storm to hit the Florida Panhandle.
2018
Camp Fire in Butte County, Calif., becomes the deadliest fire in the state's history.
2020's

2020
The Covid-19 pandemic causes a worldwide shutdown, triggering the steepest global recession in generations.

2020
Lloyd's issues an apology for its role in insuring the transatlantic slave trade.
2020
Record-breaking Atlantic hurricane season includes 30 named storms, 11 of which made landfall in the continental U.S.
2020
The U.S. experiences 22 climate and weather-related disasters totaling $1 billion each for the first time ever.
2020
The first COVID business-interruption suit was filed on March 16, 2020, by Cajun Conti, owner of the Oceana Grille in New Orleans, against a Lloyd's of London syndicate.
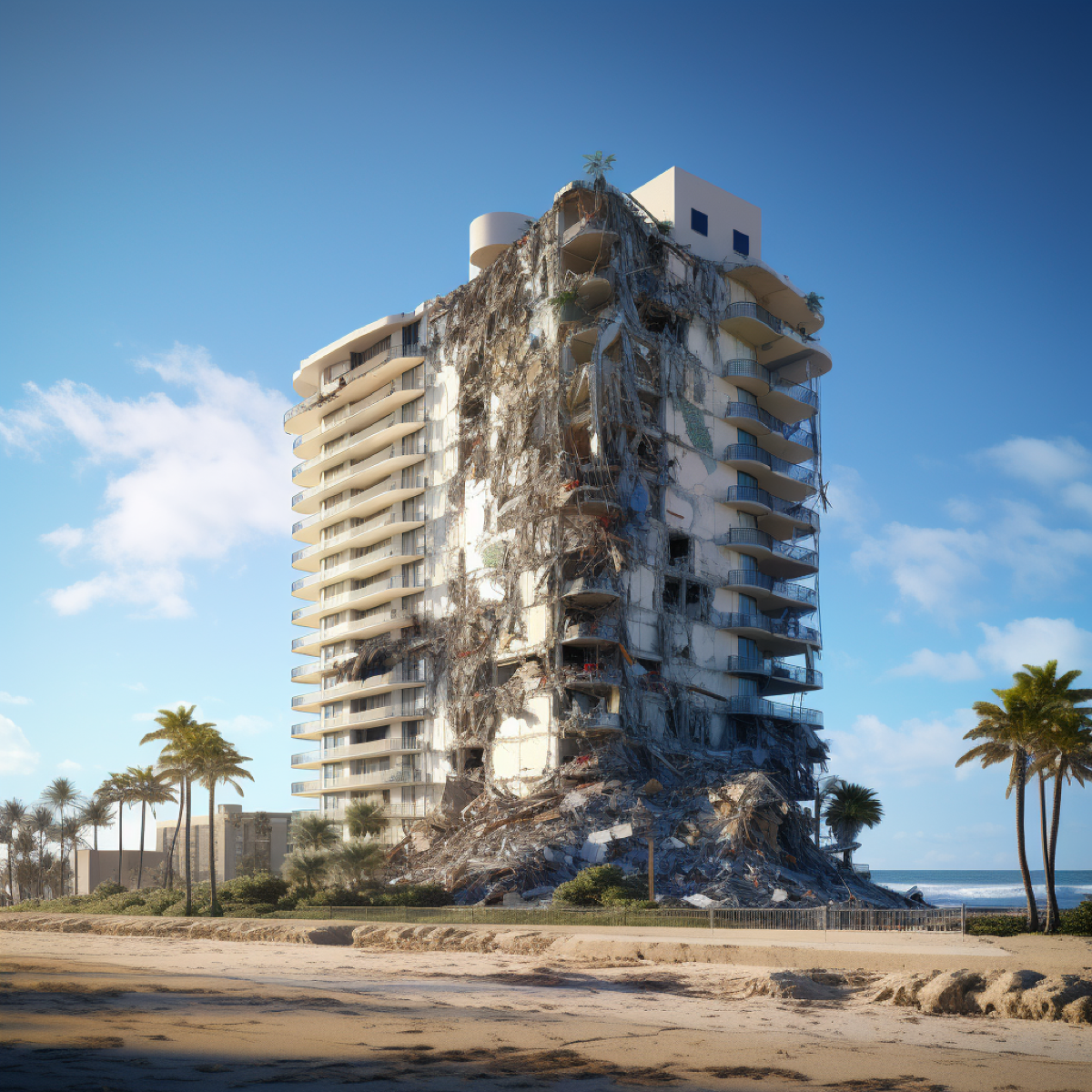

2021
Surfside condominium tower collapse in Surfside, Fla., kills 98 people.
2021
Western U.S. experiences the worst drought since 2000.

2023
World Health Organization officially declares COVID-19 is no longer a public health emergency.
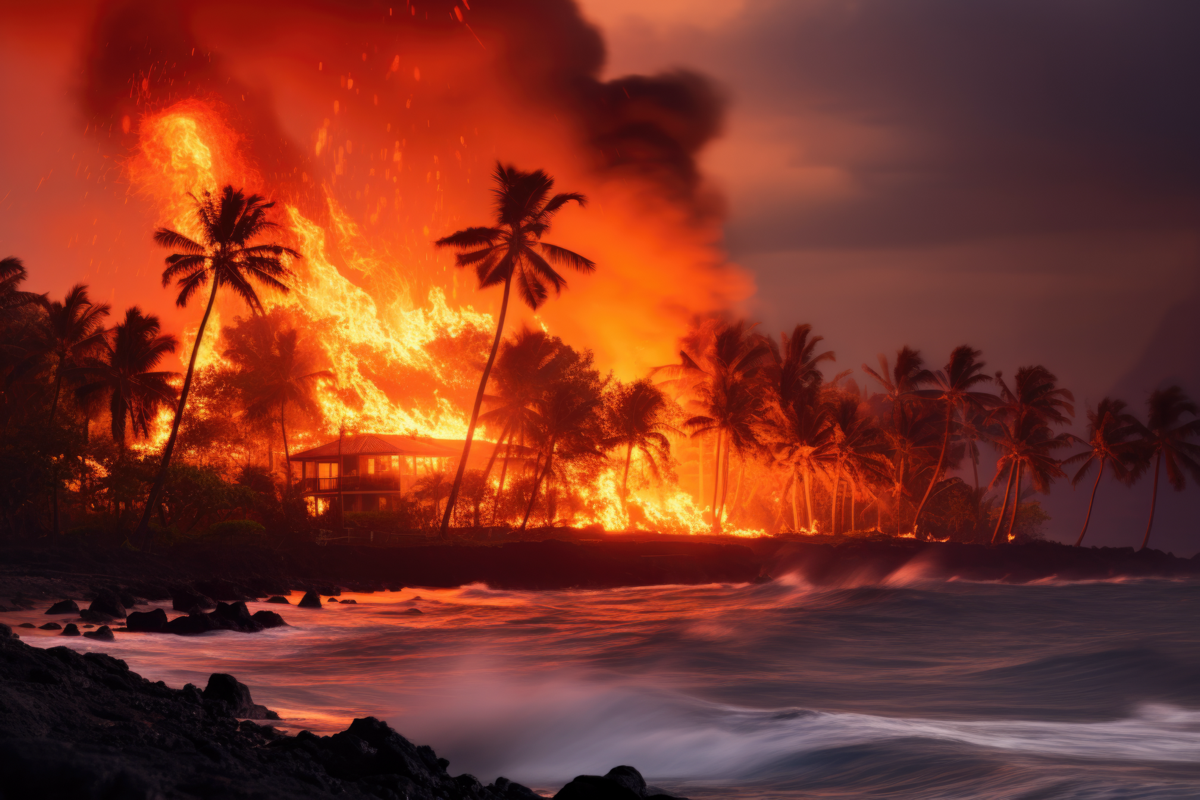

2023
Wildfire ravages Island of Maui, causing an estimated $4 to $6 billion in losses, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration predicts 2023 will be the warmest year on record. Meanwhile, the insurance industry continues to endure the hardest insurance market in a generation.

2023
Insurance Journal celebrates 100th year, gears up for many more years of delivering relevant insurance news coverage to readers.




